node.js 官方網站說 Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient
到底是什麼架構讓 node.js 可以做到 event-driven 及 non-blocking 呢?今天就來談談這個話題。
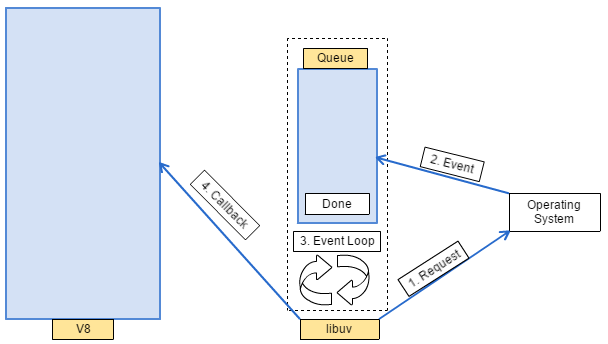
首先我們要知道 node.js 內部有個 v8 engine,它負責把 javascript 程式碼轉成電腦能執行的資訊。
另一個重要的架構是 libuv,由於有這個 library,node.js 才能實現 event-driven 及 non-blocking 特性。
假設你想用 node.js 讀一個文字檔,你可能會這麼寫
var fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('myFile.txt', function(err, data) {
console.log(data);
});
console.log('After calling readFile');
當 readFile 被調用時,libuv 會發出一個 request 給作業系統,請它回傳 myFile.txt 的內容。等到作業系統取得檔案內容後,libuv 會收到通知,當 event loop 處理這個 event 時,發現它有對應的 callback, function(err, data) { console.log(data); } 才會被調用。
這邊 event loop 做的事可以用一段 pseudo code 表示:
while there are still events to process:
e = get the next event
if there is a callback associated with e:
call the callback
由於 libuv 運作時,v8 engine 也可以同時處理 javascript 的 code,所以才說 node.js 是 non-blocking,這代表 javascript code 不需要等作業系統取得檔案內容就可以繼續下一動作。
由於每當一個 event 結束時,v8 都可以收到通知,所以才說 node.js 是 event-driven。
參考資料: